Knowledge Management
“Those who do not learn from history are condemned to repeat it”. Good practice refers to the DIKW (Data, Information, Knowledge and Wisdom) model. All too often an organization will capture the appropriate data but fail to process the data into information, synthesize the information into knowledge and then combine that knowledge with others to bring us wisdom. Wisdom will help CERN to make better decisions and improvements, but we need to capture the knowledge before we can turn it into wisdom.
The Knowledge Management process covers the lifecycle of knowledge:
- Publishing Articles (with support for multiple languages, and content and layout review workflow to assure correctness and coherent presentation format)
- Managing Articles (including collection of statistics on the usage of knowledge)
- Reviewing Articles (with regular review proces workflow to assure articles are up to date)
- Archiving Articles
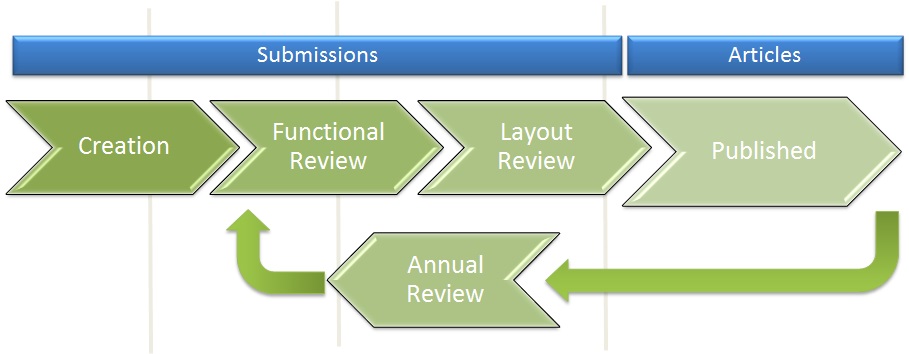
The Knowledge Management process aims at unified, standardized and repeatable handling of Knowledge Articles created by CERN.
Knowledge Management is key to continuous improvement processes for CERN Service Management activities.
Knowledge Management was rolled out in 2012 ; in Mai 2015 we have over 3000 published articles in the knowledge base.
The knowledge process and implementation is being reviewed in view of increasing simplicity of usage and reduction of maintenance effort by moving closer to 'out of the box'. The new release is intended to go live by autumn 2015.
Knowledge articles can be used to share knowledge between supporters, or can be published on the service portal which allows end users to solve their own problems, or guides users to follow the correct process.
The detailed process definition can be found here.
